Plant nitrogen uptake preference and drivers in natural ecosystems at the global scale
Nitrogen (N) is the primary nutrient element limiting the growth and productivity of terrestrial plants. Elucidating plant N acquisition is crucial for understanding plant N strategies and ecosystem productivity.
Based on the global-scale 15N tracer studies about plant N uptake strategies, researchers found that globally, the average contributions of ammonium (NH4+), nitrate (NO3-), and glycine N to the total plant N uptake were 41.6±1.1%, 32.8±1.2%, and 25.6±0.9%, respectively. However, plant N uptake preferences differed significantly among climatic regions and vegetation types, with soil NH4+ and NO3- contributed most to plant N uptake in (sub)tropical and high-latitude regions, respectively. Plant functional type was one of the most important factors driving NO3- preference, with significantly higher NO3- preference of nonwoody species than broadleaf-evergreen, conifer, and shrub species. Organic N preference was lowest in (sub)tropics and significantly lower than that in temperate and alpine regions.
This study showed clear climatic patterns and different driving factors of plant preference for soil N forms, which extend this traditional understanding of plant N uptake strategies. The results can contribute to the accurate prediction of N constraints on ecosystem productivity under global change.
For further reading, please find the paper entitled “Plant nitrogen uptake preference and drivers in natural ecosystems at the global scale”. The article link is: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-024-02603-5
The first-author (MAO Jinhua) is a researcher in South China Botanical Garden, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
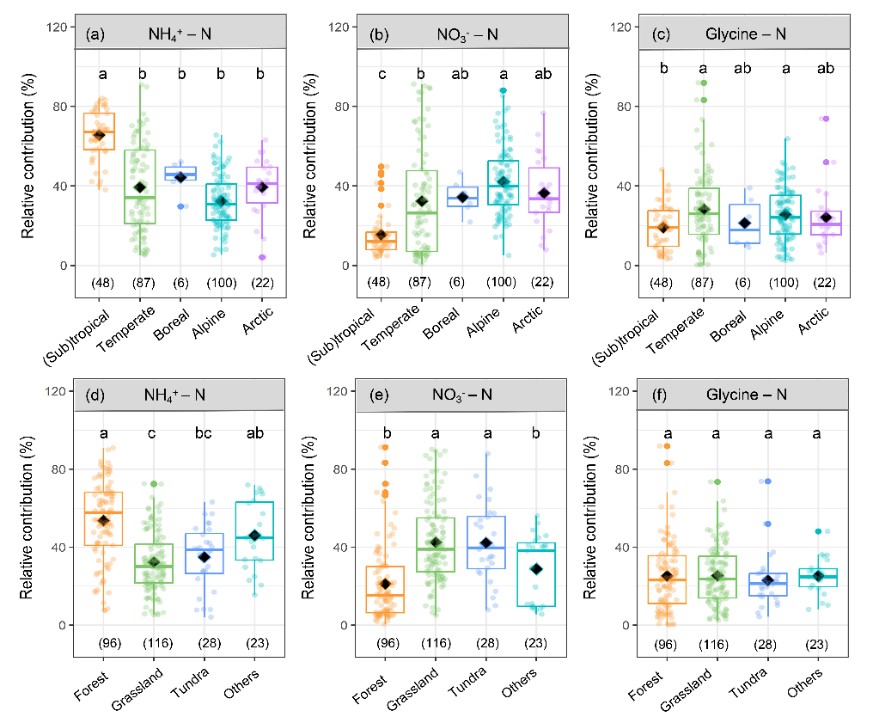
Figure 1. Relative contribution of different soil nitrogen forms to plant N uptake among climate zones and ecosystem types. (Image by Mao et al)
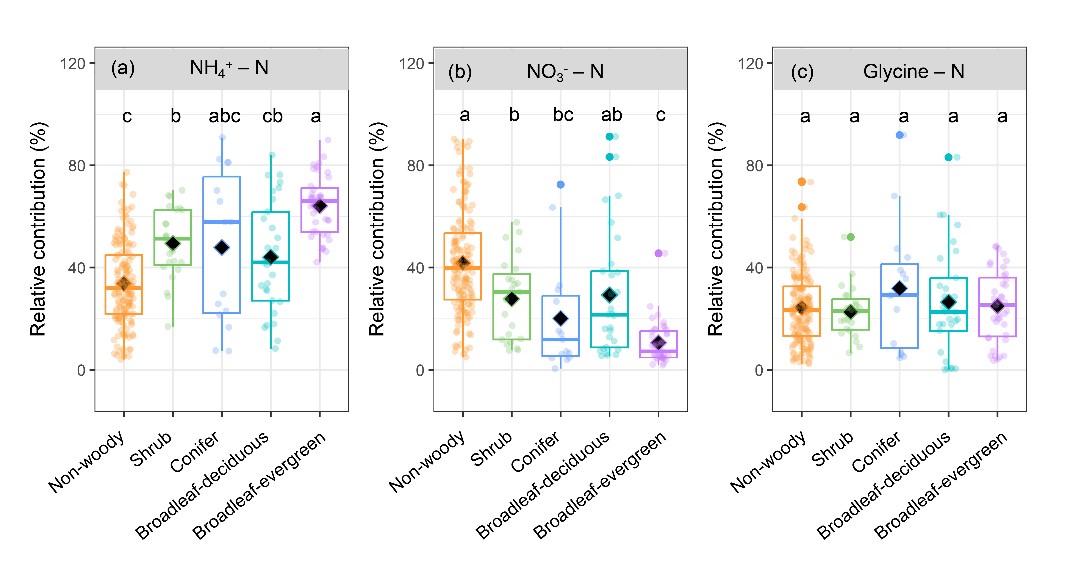
Figure 2. Relative contribution of different soil nitrogen forms to plant N uptake among plant functional types. (Image by Mao et al)
File Download: